The Web Service Consumer is an existing connector in Mule 4 that you can configure to point to a SOAP based web service. Webservice consumer call webservice hosted elsewhere as WSDL SOAP services and get response. This connector simplified process and encapsulated all the feature to consume SOAP based webservice. When no connector is available specific to any product (like Service-Now, Workday etc.), which is hosted as SOAP based webservice then this webservice consumer Connector enables any services to consume.
The main feature of this connector is
- Consuming DOC Literal Web services.
- SOAP multipart messages.
- SOAP Headers.
- DataSense support for SOAP Headers, SOAP Body, and Attachment.
- Embedded DataWeave transformations inside the operation.
- Support and Unified experience for SOAP with attachments and MTOM handling.
- Custom HTTP configuration as transport (runtime and design time).
- Web Service Security (WS Security) support.
Connector Configuration- In this section we define connector configuration to communicate with SOAP based webservice end point. By default, connector uses a simple non protected HTTP configuration to send all outgoing SOAP message. In connector configuration you can select your SOAP version from drop down and provide WSDL location. Connector extract and populates Service, Port and webservice endpoint address from WSDL file.
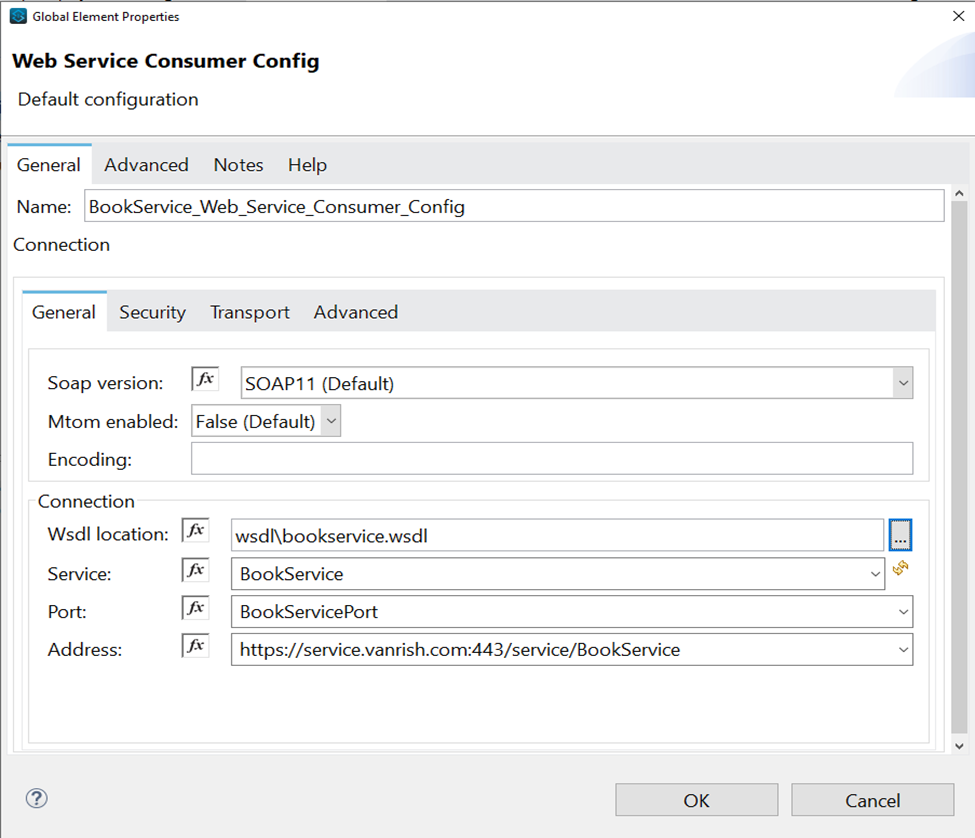
But if you are using secure endpoint address with HTTPS you need to configure custom Transportation Configuration for HTTPS.
These are the steps to enable your secure HTTPS endpoint.
- Create jks file with keytool command
keytool -keystore clientkeystore.jks -genkey -alias client - Download certificate from WSDL HTTPS endpoint and add this certificate in your JKS file with below command
keytool -importcert -file certificate.cer -keystore clientkeystore.jks -alias "Alias"- Now configure TLS Context for Webservice consumer connector.
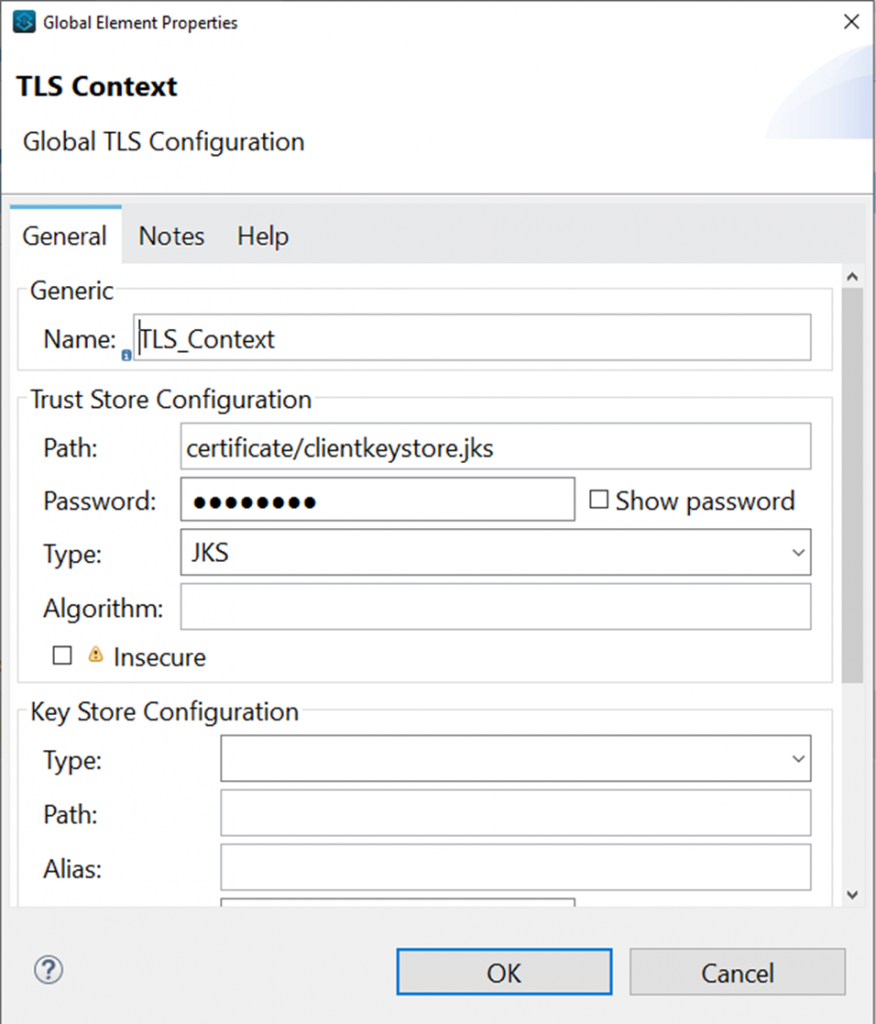
<tls:context name="TLS_Context" doc:name="TLS Context" doc:id="f634b824-2695-4d5f-8789-7a309b1511cb" >
<tls:trust-store path="certificate/clientkeystore.jks" password="xxxxxx" type="jks" />
</tls:context>- Now configure HTTP Request configuration for HTTPS endpoint.
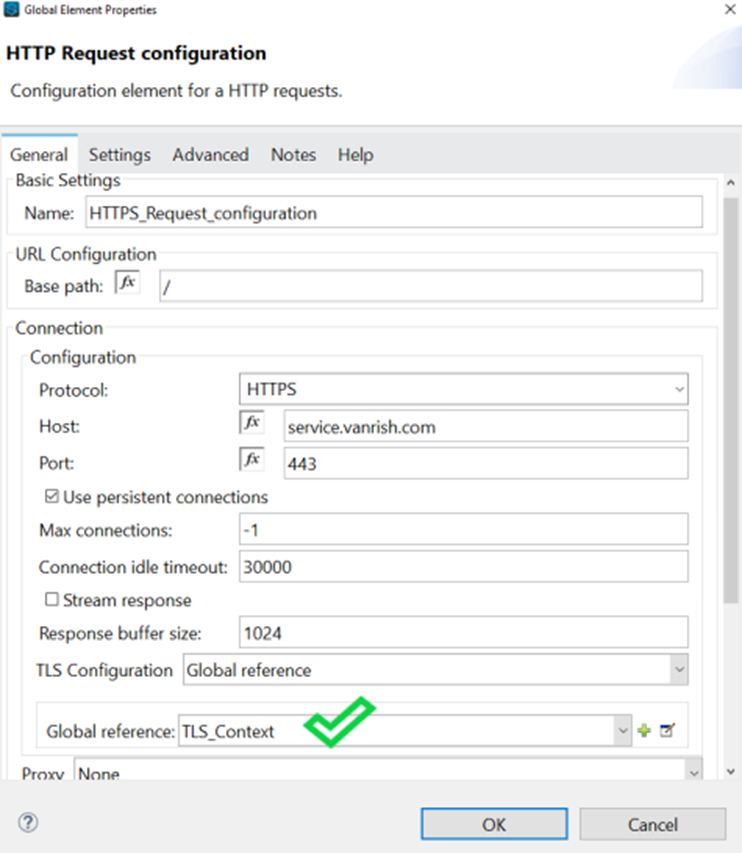
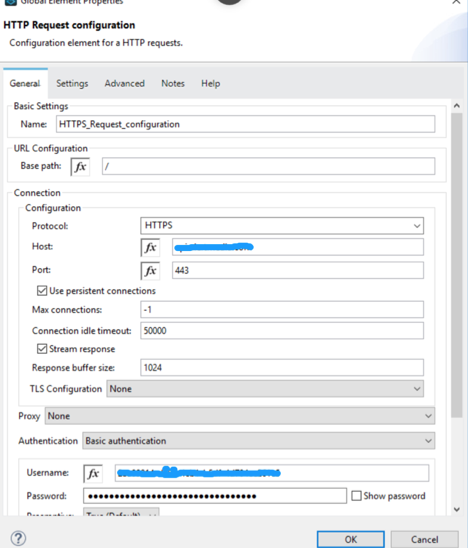
<http:request-config name="HTTPS_Request_configuration" doc:name="HTTPS Request configuration" doc:id="02db1fd9-9f04-4eae-83cf-df43effd25d2">
<http:request-connection protocol="HTTPS" host="service.vanrish.com" port="443" tlsContext="TLS_Context">
</http:request-connection>
</http:request-config>
- If TLS and HTTPS configuration configured then you can select HTTP request configuration from Webservice consumer
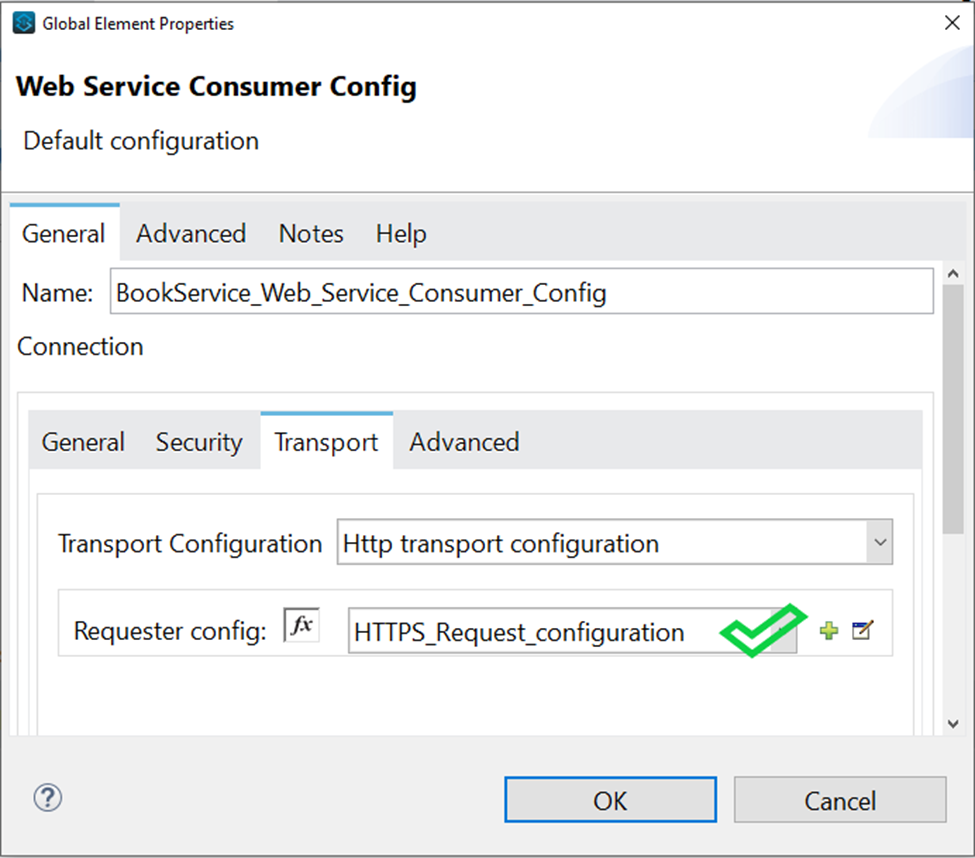
<wsc:config name="BookService_Web_Service_Consumer_Config" doc:name="Book Web Service Consumer Config" doc:id="59fd0d73-f90d-4cf0-9855-c008307067a2" >
<wsc:connection wsdlLocation="wsdl\bookservice.wsdl" service="BookService" port="BookServicePort" address="https://service.vanrish.com:443/service/BookService">
<wsc:custom-transport-configuration >
<wsc:http-transport-configuration requesterConfig="HTTPS_Request_configuration"/>
</wsc:custom-transport-configuration>
</wsc:connection>
</wsc:config>
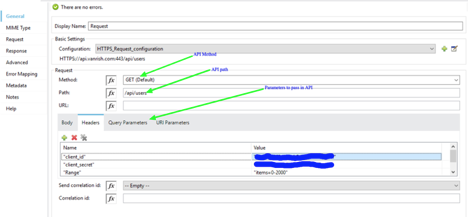
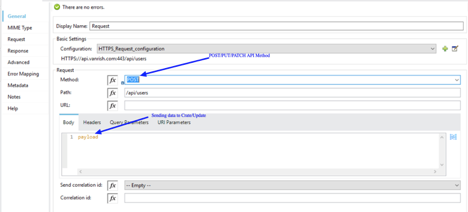
Connector Parameter- If connector configuration is configured properly, your operation parameters are available from WSDL as drop down options.
In Message section there are three parameters available
- Body – The Body is main part of the SOAP message. The body element accepts embedded DataWeave scripts as values so that you can construct the XML request without having a side effect on the message or having to use multiple components to create the request.
- Headers – The headers element contains application-specific information (like authentication, payment, and so on) about the SOAP message . This elements accepts embedded DataWeave scripts as values.
- Attachment – The attachments element enables you to bind attachments to the SOAP message. This element also accepts embedded DataWeave scripts as values.
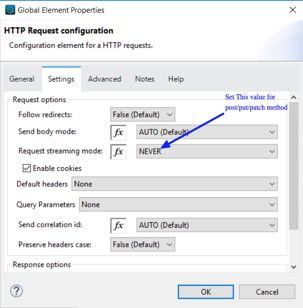
Since you configured custom HTTPS connector for your webservice consumer Connector you can configure Transport Configuration. In Transport header section you can select “Edit inline” and add all your header parameters in line
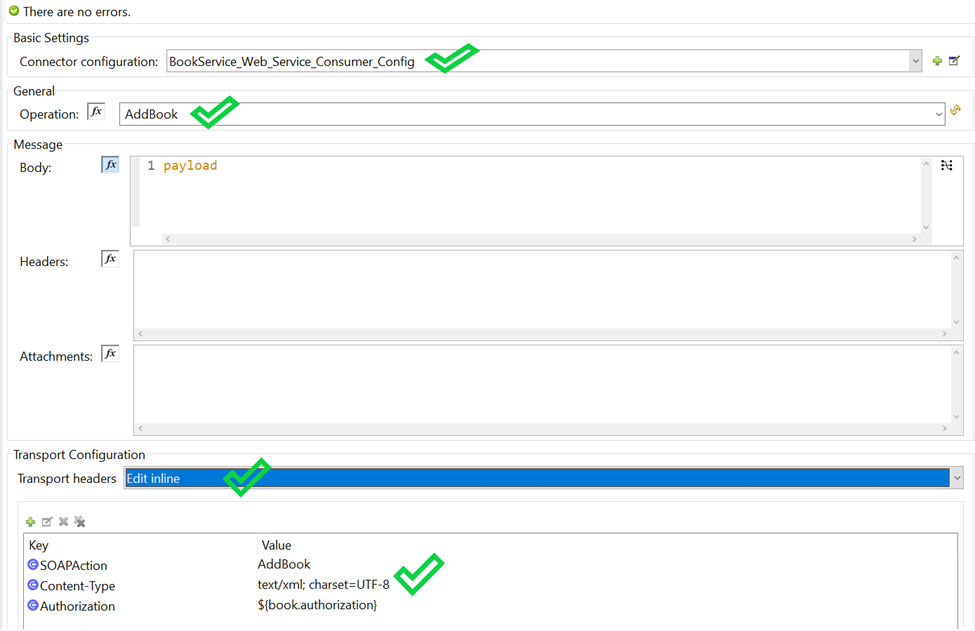
<wsc:consume doc:name="Consume" doc:id="ca5a1247-7cf6-4c7f-a442-b6fd037c13c9" config-ref="BookService_Web_Service_Consumer_Config" operation="AddBook">
<wsc:transport-headers >
<wsc:transport-header key="SOAPAction" value="AddBook" />
<wsc:transport-header key="Content-Type" value="text/xml; charset=UTF-8" />
<wsc:transport-header key="Authorization" value="${book.authorization}" />
</wsc:transport-headers>
</wsc:consume>
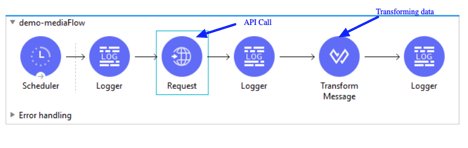
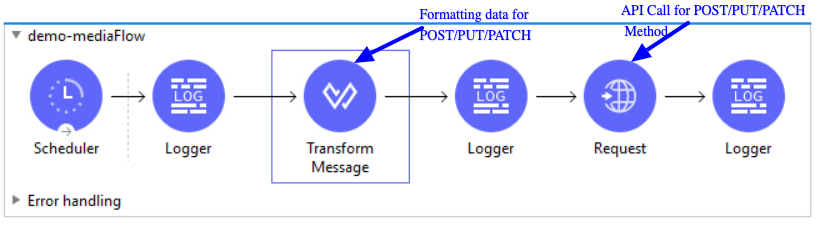
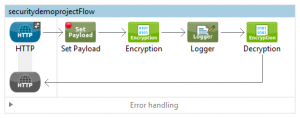
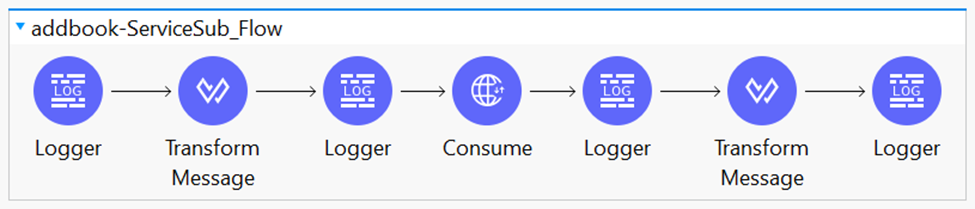
Here is webservice consumer flow diagram
Code for this flow
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns:ee="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core"
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http" xmlns:tls="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/tls"
xmlns:wsc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/wsc"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core/current/mule-ee.xsd http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/wsc http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/wsc/current/mule-wsc.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/tls http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/tls/current/mule-tls.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd">
<wsc:config name="BookService_Web_Service_Consumer_Config" doc:name="Book Web Service Consumer Config" doc:id="59fd0d73-f90d-4cf0-9855-c008307067a2" >
<wsc:connection wsdlLocation="wsdl\bookservice.wsdl" service="BookService" port="BookServicePort" address="https://service.vanrish.com:443/service/BookService">
<wsc:custom-transport-configuration >
<wsc:http-transport-configuration requesterConfig="HTTPS_Request_configuration" />
</wsc:custom-transport-configuration>
</wsc:connection>
</wsc:config>
<tls:context name="TLS_Context" doc:name="TLS Context" doc:id="f634b824-2695-4d5f-8789-7a309b1511cb" >
<tls:trust-store path="certificate/clientkeystore.jks" password="changeit" type="jks" />
</tls:context>
<http:request-config name="HTTPS_Request_configuration" doc:name="HTTPS Request configuration" doc:id="02db1fd9-9f04-4eae-83cf-df43effd25d2">
<http:request-connection protocol="HTTPS" host="service.vanrish.com" port="443" tlsContext="TLS_Context">
</http:request-connection>
</http:request-config>
<sub-flow name="addbook-ServiceSub_Flow" doc:id="511f0969-0b7d-4b7e-a113-60ef03e97648" >
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" doc:id="e6bd0106-e512-4fdd-97cf-1dbd77e1e0e7" message="Entering into AddBook flow"/>
<ee:transform doc:name="Transform Message" doc:id="06cc17de-86a9-4c53-a2f4-167d9561bed9" >
<ee:message >
<ee:set-payload ><![CDATA[%dw 2.0
output application/xml skipNullOn="everywhere"
ns n0 https://www.service.vanrish.com/BookService/
---
n0#AddBook:
{
n0#Book : {
ID: payload.id,
Title : payload.title,
Author : payload.author
}
}]]></ee:set-payload>
</ee:message>
</ee:transform>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" doc:id="ce84f628-7b38-4d2d-b5e3-9fdded2c9289" message="soap request --> #[payload]"/>
<wsc:consume doc:name="Consume" doc:id="ca5a1247-7cf6-4c7f-a442-b6fd037c13c9" config-ref="BookService_Web_Service_Consumer_Config" operation="AddBook">
<wsc:transport-headers >
<wsc:transport-header key="SOAPAction" value="AddBook" />
<wsc:transport-header key="Content-Type" value="text/xml; charset=UTF-8" />
<wsc:transport-header key="Authorization" value="${book.authorization}" />
</wsc:transport-headers>
</wsc:consume>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" doc:id="680d69e0-2b01-480c-afe7-660ca22b2f9f" message="AddBook Output-->#[payload]"/>
<ee:transform doc:name="Transform Message" doc:id="72d26561-107a-4c6e-a7d4-85bd18e0d316" >
<ee:message >
<ee:set-payload ><![CDATA[%dw 2.0
ns ns0 https://www.service.vanrish.com/BookService/
output application/json skipNullOn="everywhere"
---
payload.body.ns0#AddBookResponse]]></ee:set-payload>
</ee:message>
</ee:transform>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" doc:id="ea517185-efa4-4bf2-a03f-e8bd4d308e80" message="Output AddBook --> #[payload]"/>
</sub-flow>
</mule>
Rajnish Kumar is CTO of Vanrish Technology with Over 25 years experience in different industries and technology. He is very passionate about innovation and latest technology like APIs, IOT (Internet Of Things), Artificial Intelligence (AI) ecosystem and Cybersecurity. He present his idea in different platforms and help customer to their digital transformation journey.