Generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) is a new buzzword across the industries. Generative AI is an artificial intelligence technology that can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, audio, and synthetic data.
All organizations are investing large amounts of their budget in GenAI technology. Recently Amazon completed a $4 billion investment in generative AI development. As per a recent study barely scratching the Generative AI use case and opportunity.
Before implementing any Generative AI solution make sure you completely understand the organization’s business problem to implement Gen AI solution, because any generative AI solution takes a lot of money, time, and brain power.
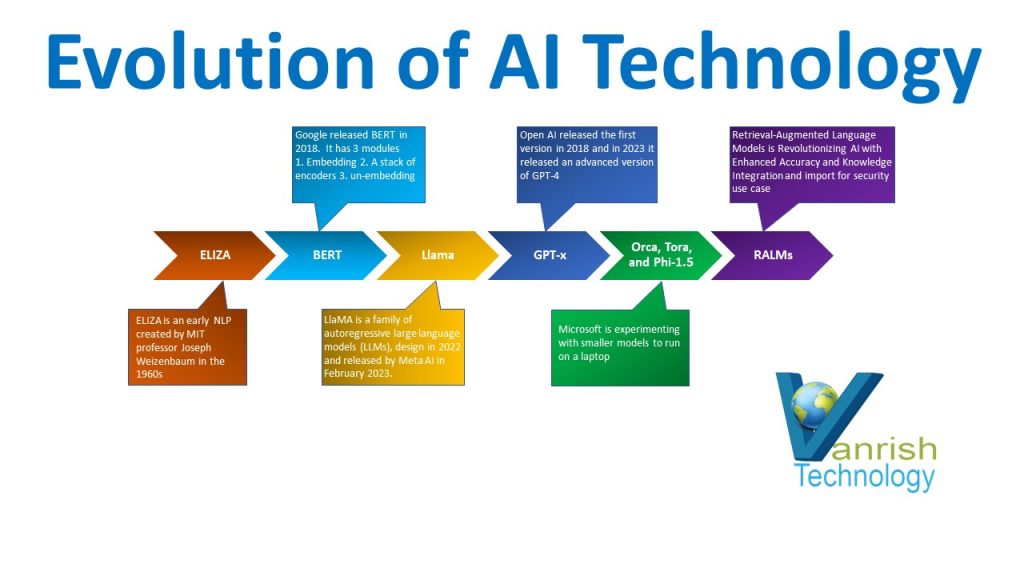
Evolution of LLMs
Generative AI has just blown up within the last year or two years, but it has been around for decades. Generative AI is based on large language models (LLM). LLM has been evolving for a while technically five to ten years approx. All companies (like AWS, Microsoft, and Open AI) are presenting their standard based on their business requirements. Here is the evolution story of LLMs & GenAI.
AI Attacks
There are four types of AI attacks.
- Poisoning – This AI attack can lead to the loss of reputation and capital. This is a classic example of thrill-seekers and hacktivists injecting malicious content which subsequently disrupts the retraining process.
- Inference – This AI attack can result in the leakage of sensitive information. This attack aims to probe the machine learning model with different input data and weigh the output.
- Evasion – This AI attack can harm physical safety. This type of attack is usually carried out by Hacktivists aiming to get the product of a competitive company down and has the potential to seriously harm the physical safety of people.
- Extraction – This AI attack can lead to insider threats or cybercriminals. Based on this the attacker can extract the original model and create a stolen model to find evasion cases and fool the original model.
Type of AI Malware
- Black Mamba – Black Mamba utilizes a benign executable that reaches out to a high-reputation API (OpenAI) at runtime, so it can return synthesized, malicious code needed to steal an infected user’s keystrokes. It has the below properties.
- ChatGPT Polymorphic Malware
- Dynamically Generates Code
- Unique Malware code
- Deep Locker – The Deep Locker class of malware stands in stark contrast to existing evasion techniques used by malware seen in the wild. It hides its malicious payload in benign carrier applications, such as video conference software, to avoid detection by most antivirus and malware scanners. It has the below properties.
- Targeted identification
- Logic detonation Mechanism
- Facial and voice recognition
- MalGAN – Generative Adversarial Networks serve as the foundation of Malware GAN and are used to create synthetic malware samples. For Mal-GAN’s complex design to function, it is made up of three essential parts: the generator, substitute detector, and malware detection system based on machine learning. It has the below properties.
- Generative Adversarial Malware
- Bypass ML-based Detections
- Feed-forward Neural Networks
AI Security Threats
- Deepfake Attacks
- Mapping and Stealing AI Models
- Spear Phishing (Deep Phishing)
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- DDoS and Scanning of the Internet.
- Data poisoning AI Models
- PassGAN and MalGAN
- Auto Generation of Exploit code
- Ransom Negotiation Automation
- Social Engineering
AI Security Defense Strategy
As we learned in AI several AI malware and threats are impacting different parts of the AI ecosystem. Our AI must be smart enough that it detects its threats and mitigates risk. ML-based malware detectors detect risk and generate insights into its severity. Here are a few approaches should implement to protect your AI systems.
- Intelligent Automation
- Automated response and Mitigation
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) extraction and correlation
- Behavioral and anomaly detection
- Precision Approach
- High Accuracy and Precision
- Identify, Understand, and Neutralize
- Prioritize Risk
- Define the Area for defense
- Identify the most vulnerable area.
- Apply a broad spectrum of defense.
- System resiliency
AI involvement in security
- Malware detection – AI systems help prevent phishing, malware, and other malicious activities, ensuring a high-security posture and analyzing any unusual behavior.
- Breach risk prediction – Identify the most vulnerable system and protect against any data leak.
- Prioritize critical defense – AI-powered risk analysis can produce incident summaries for high-fidelity alerts and automate incident responses, accelerating alert investigations.
- Correlating attack patterns – AI models can help balance security with user experience by analyzing the risk of each login attempt and verifying users through behavioral data, simplifying access for verified users
- Adaptive response – AI model automated response and generate an alert if the system identifies any threats. This creates the first layer of security defense.
- Applied Machine learning – AI models are self-train. If models identify any new risk pattern apply new security models to all protected systems.
Rajnish Kumar is CTO of Vanrish Technology with Over 25 years experience in different industries and technology. He is very passionate about innovation and latest technology like APIs, IOT (Internet Of Things), Artificial Intelligence (AI) ecosystem and Cybersecurity. He present his idea in different platforms and help customer to their digital transformation journey.


